Parameters
| Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| x | An array of x coordinate values defining points of a polygonal area on the image. (in pixels) * |
| y | An array of y coordinate values defining points of a polygonal area on the image. (in pixels) * |
| Points | The number of points defining the polygonal area on the image. |
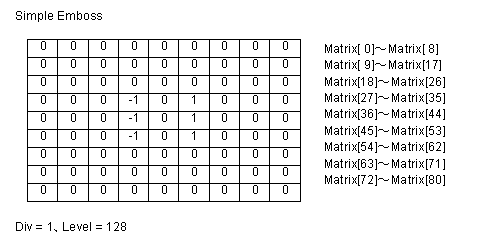
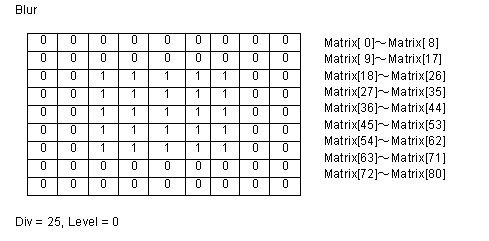
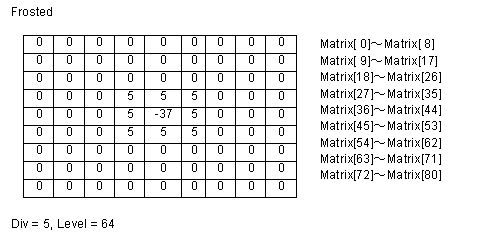
| Matrix | 9x9 matrix (an array of 81 items ranging from 0 to 80). In Visual C++, pass the pointer to the first element in the matrix array. In Visual Basic, Dim Mt(0 To 80) As Long, the arguments are returned in the first element of the array Mt(0) |
| Div | The division factor |
| Level | The bias factor (from 0 to 255, as this factor increases, the color becomes brighter) |
| Red | To process the red plane, set toTrue (nonzero), otherwise set to False (0) |
| Green | To process the green plane, set toTrue (nonzero), otherwise set to False (0) |
| Blue | To process the blue plane, set toTrue (nonzero), otherwise set to False (0) |
| * In Visual C++, pass the pointer to the first element in the x and y arrays. In Visual Basic, the arguments are returned in the first elements of the arrays x(0) and Y(0). |
|
Return Value
Returns True (nonzero) if successful, otherwise returns False (0).
Explanation
The CustomFilter method allows you to create a custom
effects filter for raster images. An effects filter alters each
pixel's color based on its current color and the colors of any
neighboring pixels. (See the explanation of the filter matrix
below.)
To execute the CustomFilter method, set the image handle of
the image in the ImageHandle property or the
Layer(LayerNo).ImageHandle
property. The CustomFilter method supports 8-bit grayscale,
16, 24, and 32 bit images.
Before executing the CustomFilter method, you must set the
area on the image that will be affected. There are 4 ways to do
this.
- To use a mask image, set the SelectMode property to 0. Set the mask image handle in the MaskImageHandle property
- To process the total image, set the SelectMode property to 1
- To process the polygonal area on the image, set the SelectMode property to 2. Select the polygon by setting the appropriate coordinate values for the points of the polygon in two arrays, one array for the x coordinate values and one array for the y coordinate values. The pass these arrays to the x and y arguments of the CustomFilter method. The number of points defining the polygon must be 3 or more
- To process an elliptical area on the image, set the SelectMode property to 3. Select the ellipse by setting the appropriate values for the bounding rectangle in the RectLeft, RectTop, RectRight, and RectBottom properties
When the SelectMode
property is set to values other than 2 (ikEffectPolygon), please
set dummy arrays in the x and y parameters and set the Points
parameter to 0. When processing a grayscale image the Red, Green
and Blue parameter values are disabled. (dummy values). When the
SelectMode property is set to
2 or 3, the appropriate value must be set in the InOut property. If successful the
resulting raster image data is set in the LayerNo property (the ImageHandle property or the
Layer(LayerNo).ImageHandle
property. If unsuccessful, 0 is returned.
When the Caption, Message, and ButtonName properties are blank, the
progress dialog box will not be displayed. When the progress dialog
box is displayed, the percentage that the processing has completed
will be shown in the dialog box.
For scripting languages and other programs that require variant
types, please refer to the CustomFilterVariant method.
The filter consists of an array of coefficients called a filter
matrix. A filter processes an image on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Each
pixel's color value is multiplied by the coefficient in the matrix
center, and any pixels within the matrix are multiplied by the
corresponding coefficients. The sum of the products becomes the
target pixel's new value. To make the filter matrix, it is
necessary to create an array containing 80 elements and set the
appropriate coefficient values in the array elements. The formula
used to calculate the target pixel's value is given below:
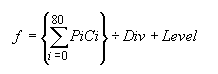
Where F is the output value of the target pixel, Pi is a pixel in
the grid, and Ci is a coefficient in the matrix. Div is the
division factor which allows you to achieve effects that would
otherwise require decimal coefficients. Level is a bias factor. You
use the bias to shift the value of each pixel by a fixed amount. As
the bias factor increases, the resultant color is brighter. Bias
adjustments are particularly useful for creating embossing
effects.
Some sample matrix are given below: