Saving Protection Information in the Registry
With the Set Password Protection tool, you can save necessary protection information, like number of days, number of uses, random indentifiers, etc., in both the registry and to file. The screenshot of the Set Password Protection tool below shows how to set the registry keys. (See area indicated in red)
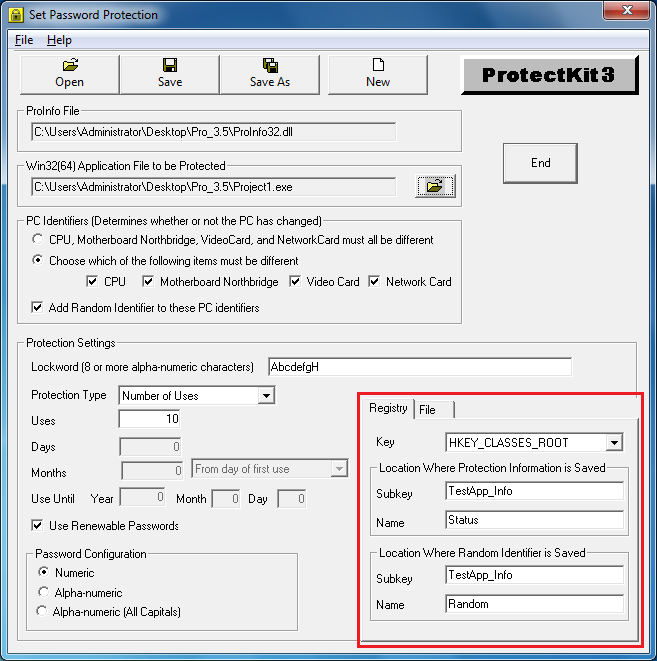
Being able to set protection information in both registry and file gives you added protection. If the enduser happens to delete the protection information from the registry, it will still remain in the file and can be restored to the registry. Likewise, if the file with the saved protection information is deleted, it can be restored from the information stored in the registry.
How to Save Information To Registry
(please refer to the above screenshot)
1. "Key" - This sets the main key in the registry where the
protection information is stored.
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE
2. "Location Where Protection Information is Saved "
SubKey - This sets the registry subkey where the protection information is stored.
Name - The name of the key where the values are stored.
3. "Location Where Random Identifier is Saved"
SubKey - This sets the registry subkey where the random identifier is stored.
Name - The name of the key where the
values are stored.
If the subkey does not exist, it will be created in the registry.
IMPORTANT!!
Be sure to set the registry keys in such a way that their
meaning is not easily understood. Use deep level hierarchy and make
sure that the name of the subkeys cannot be inferred from the name
of the application.